
02/04/21 17:00 PM IST

Why do scientists study fundamental particles?
Studying what humans and everything around them is made up of gives scientists a window into understanding the universe a better way, just how it is easy to grasp what a cake is once one knows the ingredients it is made up of.
This is one reason why scientists are so keen on studying neutrinos (not the same as neutrons), which are also a type of fundamental particle. Fundamental means that neutrinos, like electrons, protons and neutrons cannot be broken down further into smaller particles.
When the construction of telescope started ?
The construction of this telescope, which started in 2016, is motivated by the mission to study in detail the elusive fundamental particles called neutrinos and to possibly determine their sources. Studying this will aid scientists’ understanding of the origins of the universe since some neutrinos were formed during the Big Bang, others continue to be formed as a result of supernova explosions or because of nuclear reactions in the Sun.
The Baikal-GVD is one of the three largest neutrino detectors in the world along with the Ice Cube at the South Pole and ANTARES in the Mediterranean Sea.
Where do neutrinos fit in?
What makes neutrinos especially interesting is that they are abundant in nature, with about a thousand trillion of them passing through a human body every second. In fact, they are the second most abundant particles, after photons, which are particles of light. But while neutrinos are abundant, they are not easy to catch, this is because they do not carry a charge, as a result of which they do not interact with matter.
A website developed by the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory in the US says that neutrinos are “a clue to new physics: ways of describing the world that we don’t know yet. They also might have unique properties that would help explain why the universe is made of matter instead of antimatter.” Just like the subatomic particles of the so-called “normal matter” can be classified into electrons, protons and neutrons, the subatomic particles that make up antimatter have properties that are opposite to the normal matter. While it is known that antimatter exists, we do not yet know why it exists or how different the properties of its subatomic particles are from those of normal matter.
One way of detecting neutrinos is in water or ice, where neutrinos leave a flash of light or a line of bubbles when they interact. To capture these signs, scientists have to build large detectors. An underwater telescope such as the GVD is designed to detect high-energy neutrinos that may have come from the Earth’s core, or could have been produced during nuclear reactions in the Sun.
Who discovered neutrino?
Neutrinos carry no electric charge. Predicted in 1931, neutrinos were detected for the first time in 1959, and are now considered to be the second most abundant particle in the universe — after the photon, or light particle. Groups in many countries are carrying out research on neutrinos, believed to hold important clues to some of the basic questions on the universe. Research on neutrinos has led to award of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2002 and 2015, and before that, in 1988 and 1995.
A neutrino is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small (-ino) that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction.
Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected.
How Neutrino are produced in nature ?

17 Sep
'Dehradun and several other districts in Uttarakhand have experienced very heavy rainfall over the past few days, triggering landslides in multiple areas and causing rivers to swel
Read More
08 Sep
'The Rajasthan Coaching Centres (Control and Regulation) Bill, 2025, is a significant piece of legislation passed by the Rajasthan Assembly to regulate and oversee the state's burg
Read More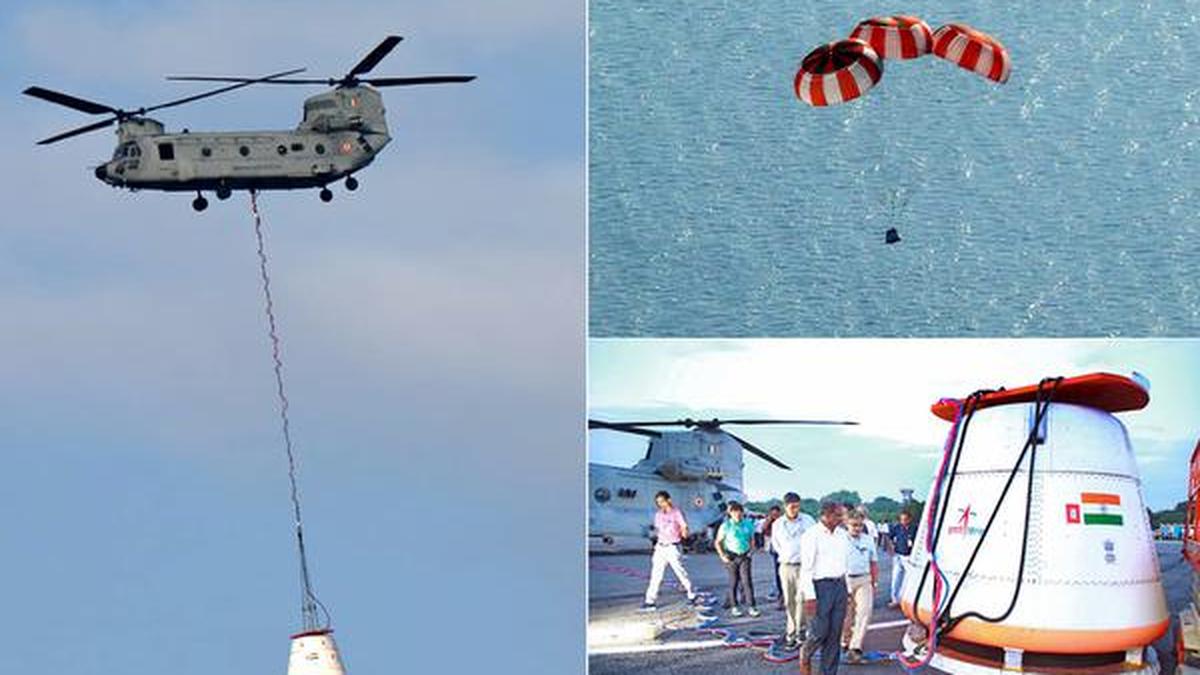
28 Aug
'Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully carried out its first Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-1), a crucial milestone in the preparation for the countr
Read More