
07/03/24 07:07 AM IST


17 Sep
'Dehradun and several other districts in Uttarakhand have experienced very heavy rainfall over the past few days, triggering landslides in multiple areas and causing rivers to swel
Read More
08 Sep
'The Rajasthan Coaching Centres (Control and Regulation) Bill, 2025, is a significant piece of legislation passed by the Rajasthan Assembly to regulate and oversee the state's burg
Read More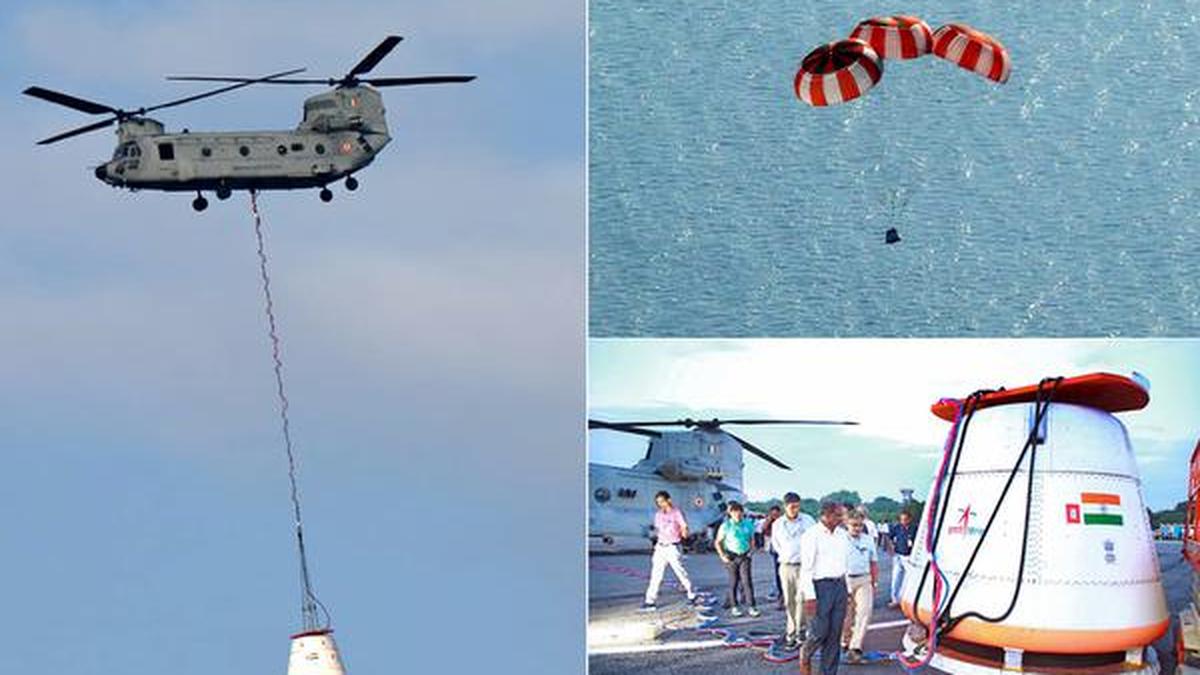
28 Aug
'Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully carried out its first Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-1), a crucial milestone in the preparation for the countr
Read More